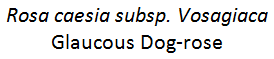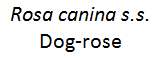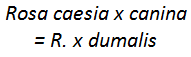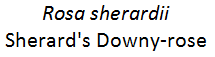Rosa species - Dog-rose
Dog-roses are interesting to study. They hybridise readily and a hybrid from the same parents may appear different depending on whether which parent was male and female!
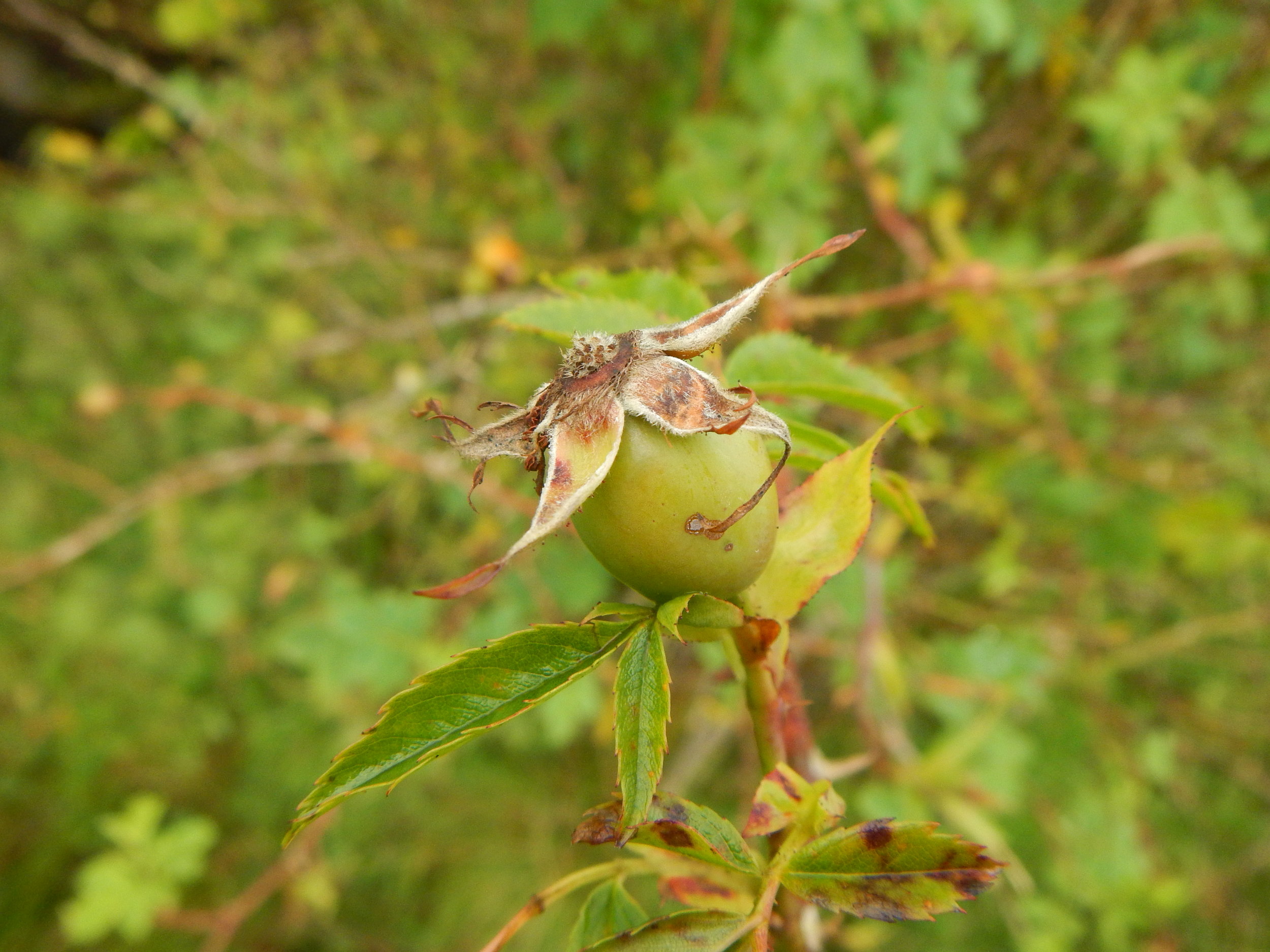
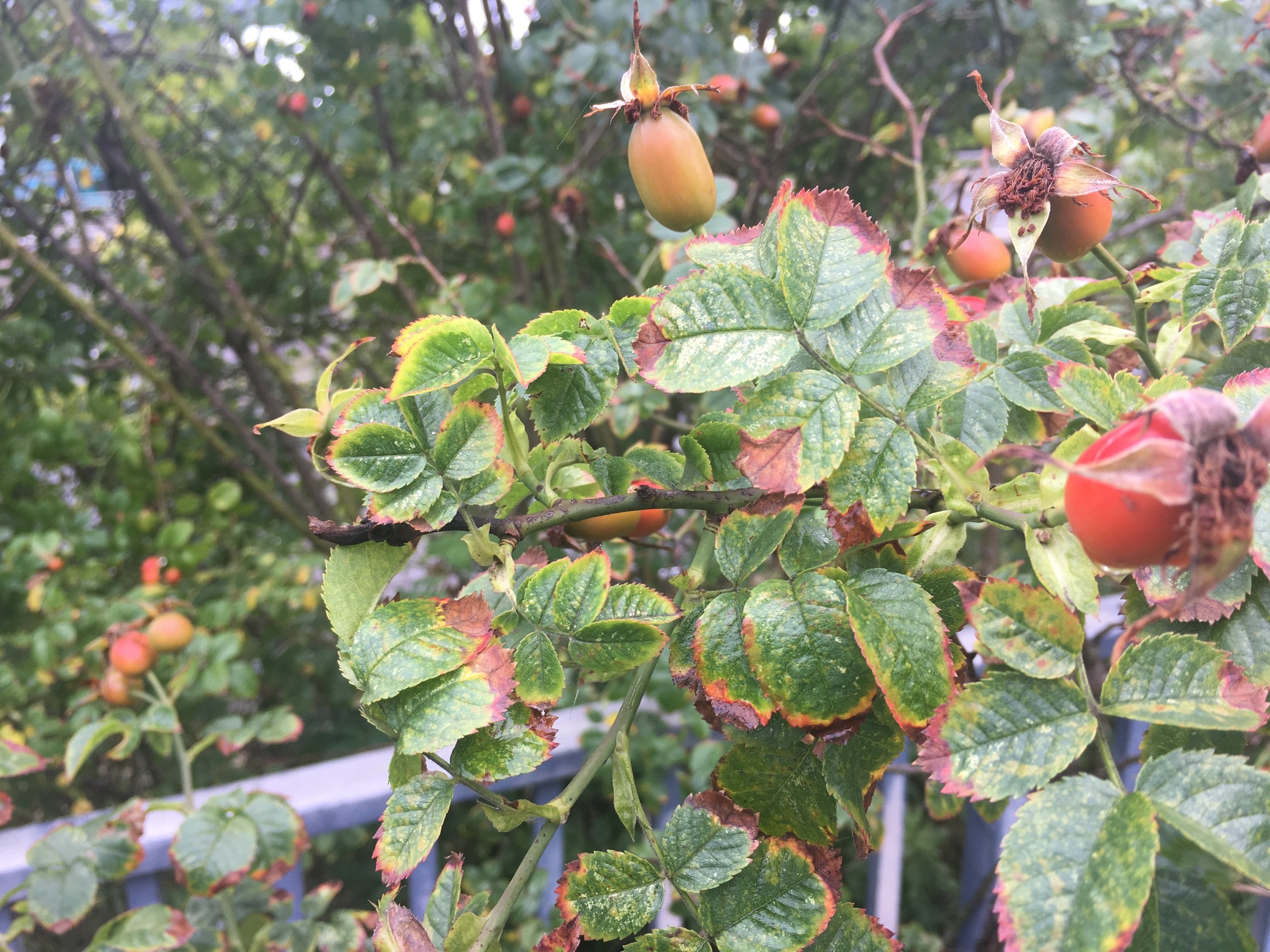
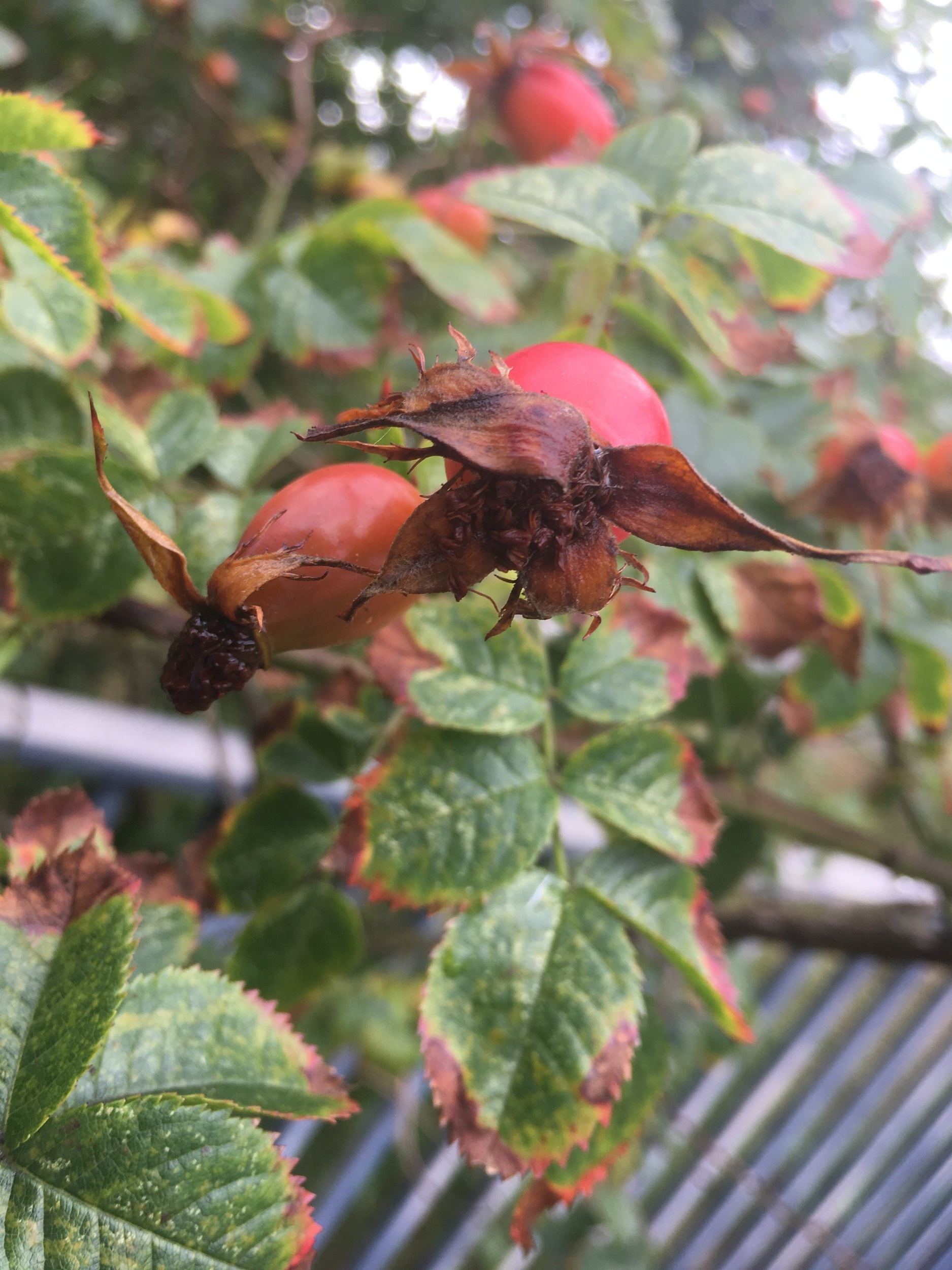
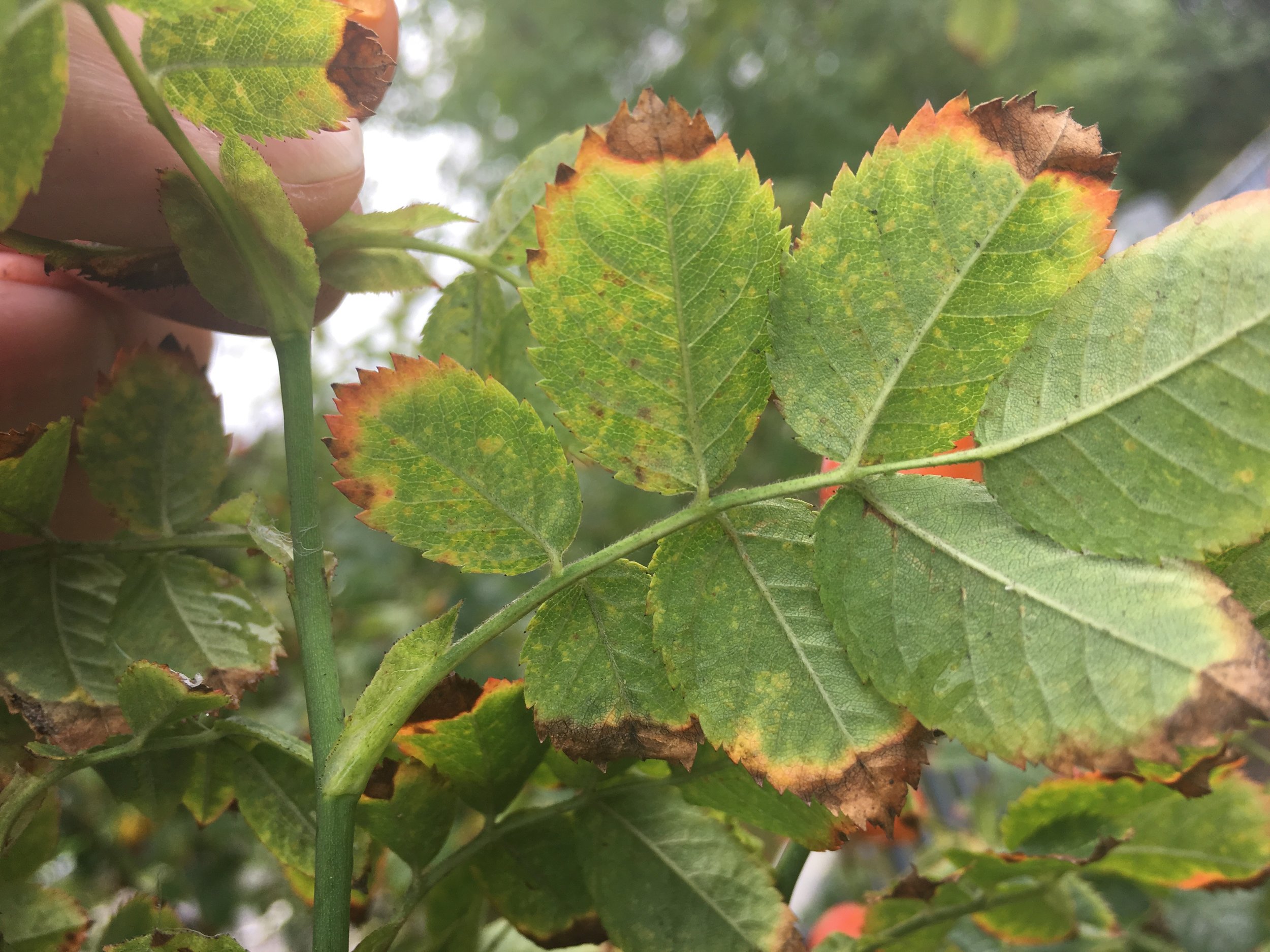
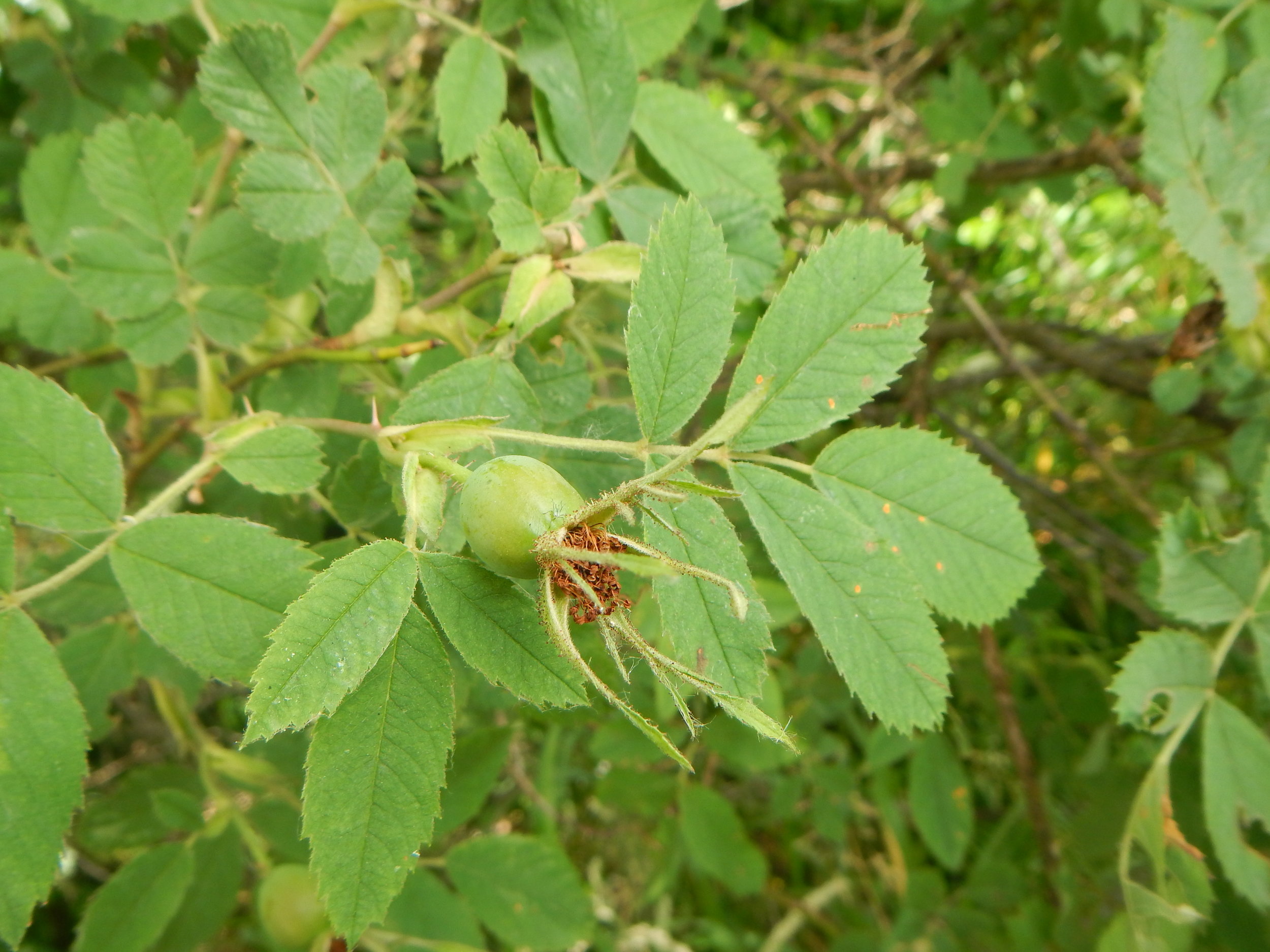
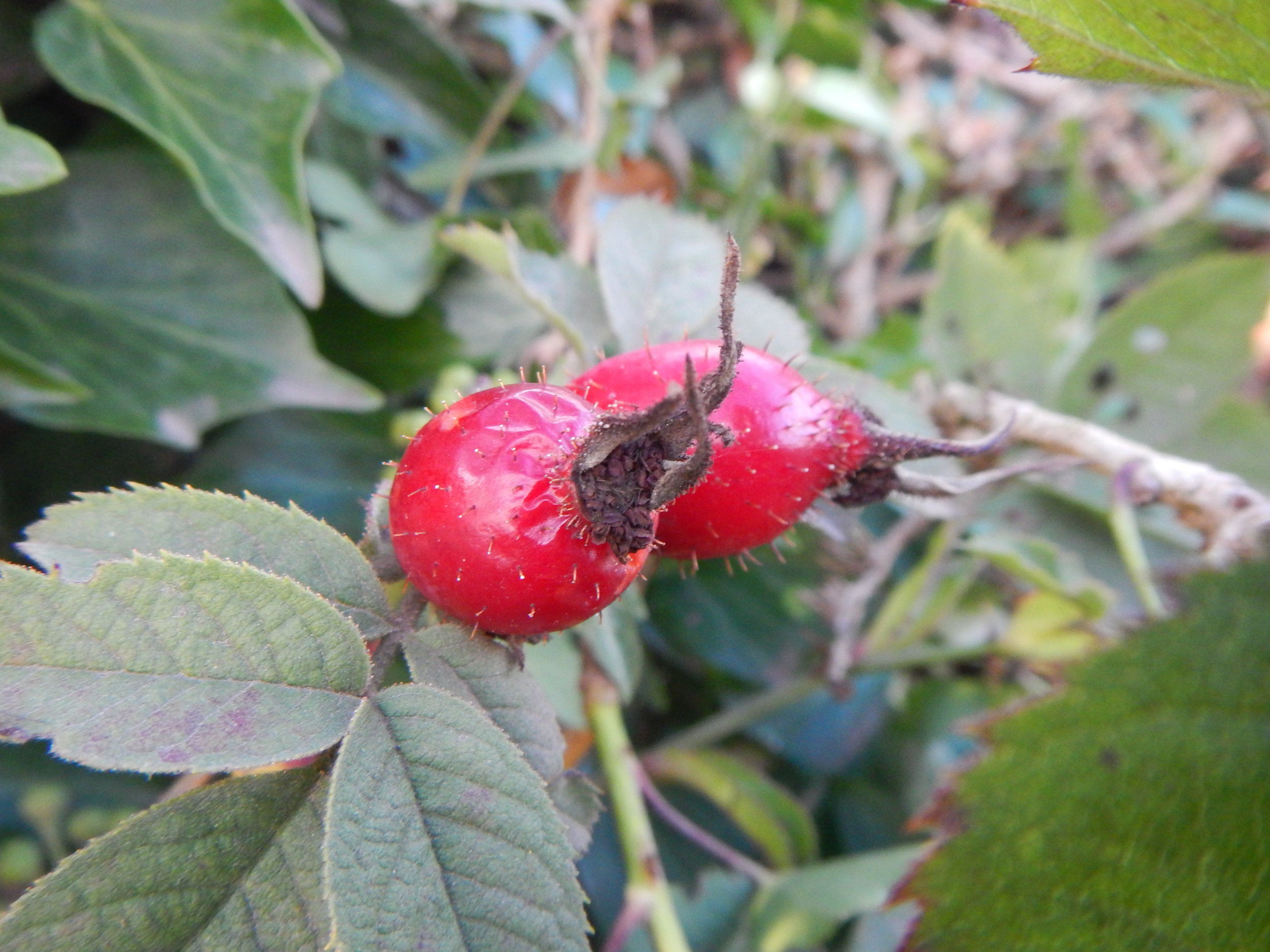
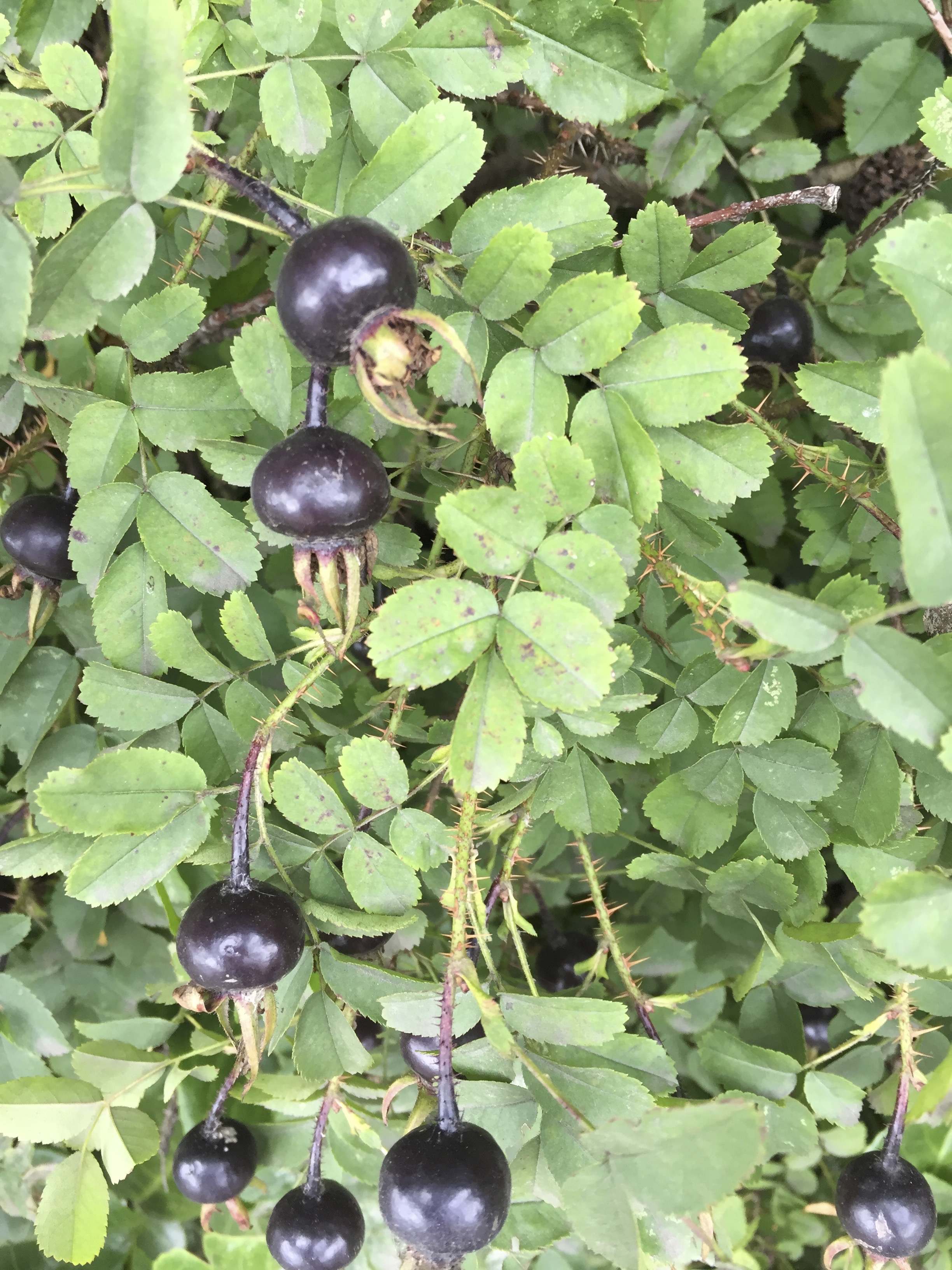
To identify you generally need hips, leaves and several stems with thorns.
Rosa canina s.s. - Dog-rose
Rosa dumalis (Previously R. caesia x canina = R. x dumalis)
Rosa caesia subsp. vosagiaca (Previously R. caesia subsp. vosagiaca) - Glaucous Northern Dog-rose
Rosa sherardii - Sherard’s Downy Rose
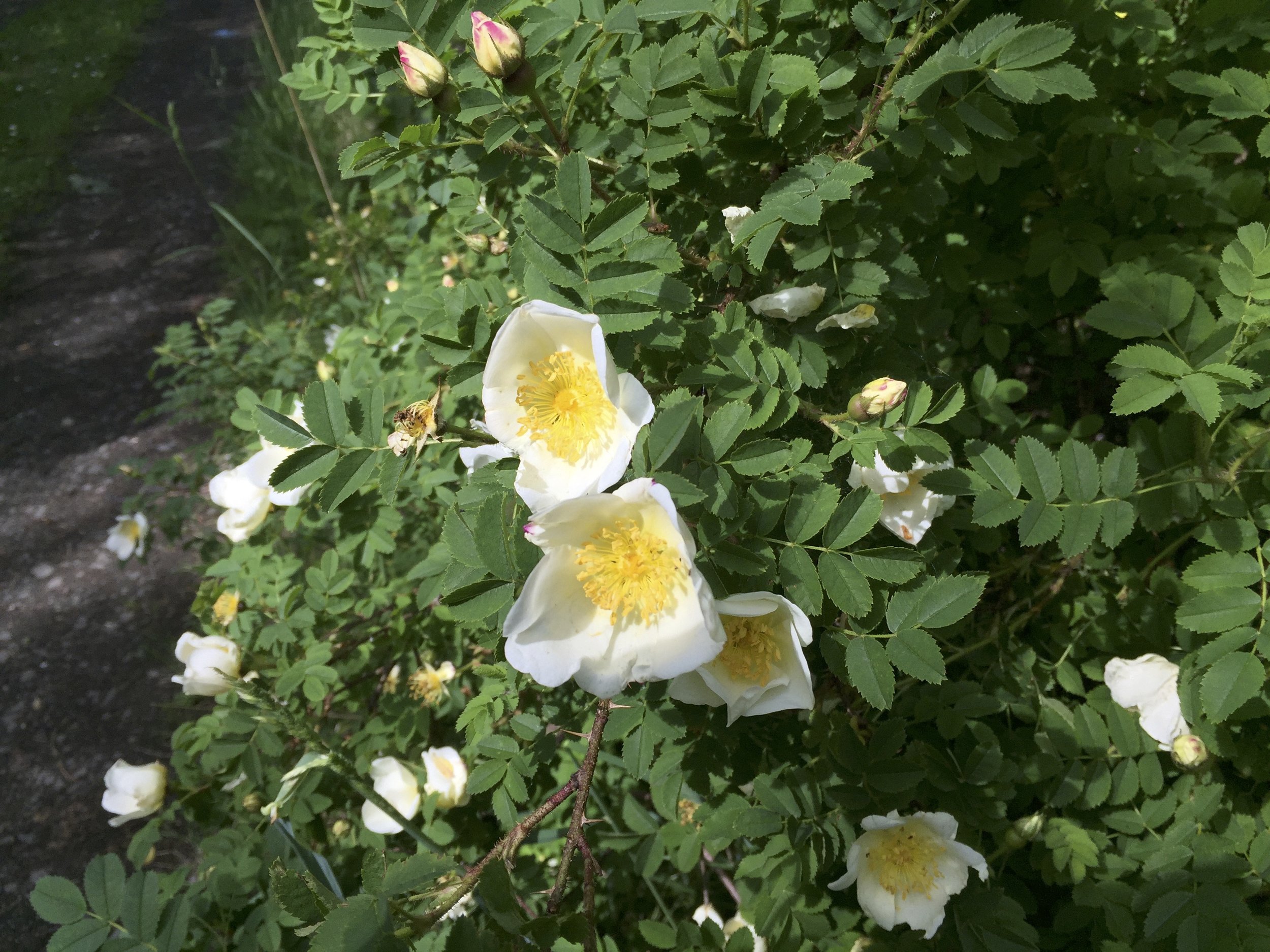
Rosa spinosissima (= Rosa pimpinellifolia) - Burnet Rose
Rosa mollis - Soft Downy-rose
The main features of this rose are:
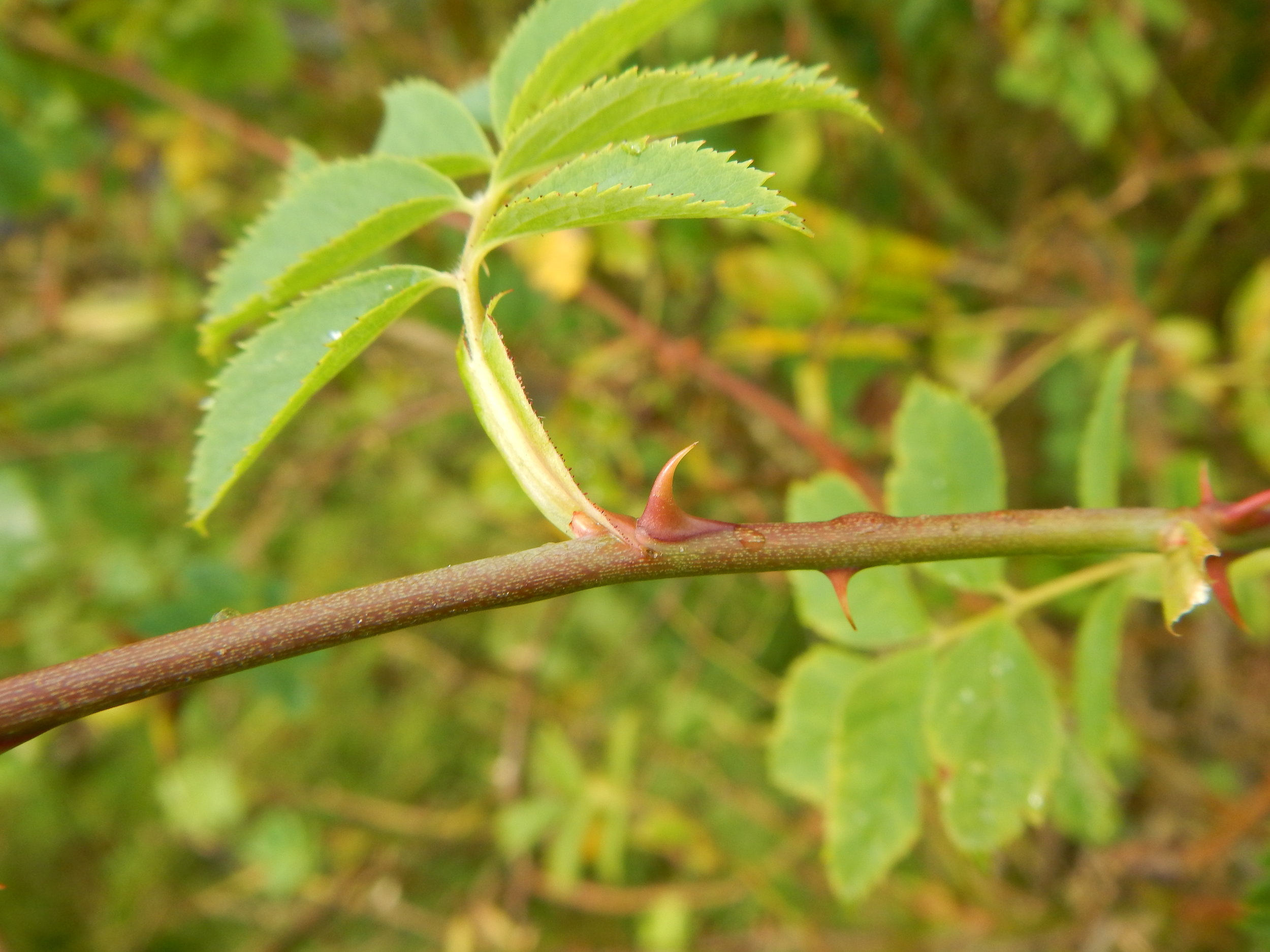
Straight thorns.
The sepals on top of the hips are erect.
There are glandular hairs on the hip and leaf stalks.
The undersurface of the leaves has a fine coating of dense hairs.
Rosa rugosa - Japanese Rose
This distinctive rose is usually planted but does become established and spreads especially in dunes.
It has dense straight prickles of widely varying sizes .The smallest of which can be tipped with glands.
The leaves are dark, crinkly and white below. They have rounded blunt serrations.
The flowers are a distinctive purplish-pink and sometimes are white in cultivars.
The hips are large compressed spheres with erect sepals and their stalks are bent so that the hips point downwards.
There are glandular hairs on stalks of hips and leaves and they can also be finely hairy.